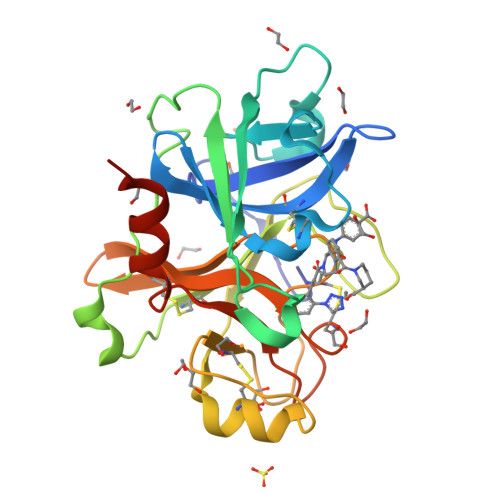
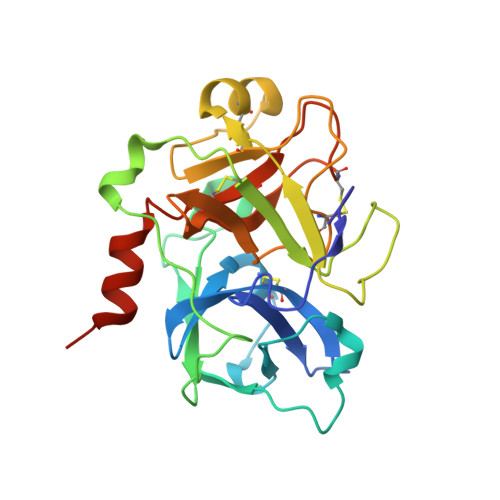
Discovery of a Parenteral Small Molecule Coagulation Factor XIa Inhibitor Clinical Candidate (BMS-962212).
Pinto, D.J.P., Orwat, M.J., Smith, L.M., Quan, M.L., Lam, P.Y.S., Rossi, K.A., Apedo, A., Bozarth, J.M., Wu, Y., Zheng, J.J., Xin, B., Toussaint, N., Stetsko, P., Gudmundsson, O., Maxwell, B., Crain, E.J., Wong, P.C., Lou, Z., Harper, T.W., Chacko, S.A., Myers, J.E., Sheriff, S., Zhang, H., Hou, X., Mathur, A., Seiffert, D.A., Wexler, R.R., Luettgen, J.M., Ewing, W.R.(2017) J Med Chem 60: 9703-9723
- PubMed: 29077405
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01171
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5QCK, 5QCL, 5QCM, 5QCN - PubMed Abstract:
Factor XIa (FXIa) is a blood coagulation enzyme that is involved in the amplification of thrombin generation. Mounting evidence suggests that direct inhibition of FXIa can block pathologic thrombus formation while preserving normal hemostasis. Preclinical studies using a variety of approaches to reduce FXIa activity, including direct inhibitors of FXIa, have demonstrated good antithrombotic efficacy without increasing bleeding. On the basis of this potential, we targeted our efforts at identifying potent inhibitors of FXIa with a focus on discovering an acute antithrombotic agent for use in a hospital setting. Herein we describe the discovery of a potent FXIa clinical candidate, 55 (FXIa K i = 0.7 nM), with excellent preclinical efficacy in thrombosis models and aqueous solubility suitable for intravenous administration. BMS-962212 is a reversible, direct, and highly selective small molecule inhibitor of FXIa.
Organizational Affiliation:
Research and Development, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company , P.O. Box 5400, Princeton, New Jersey 08543, United States.